The Problem
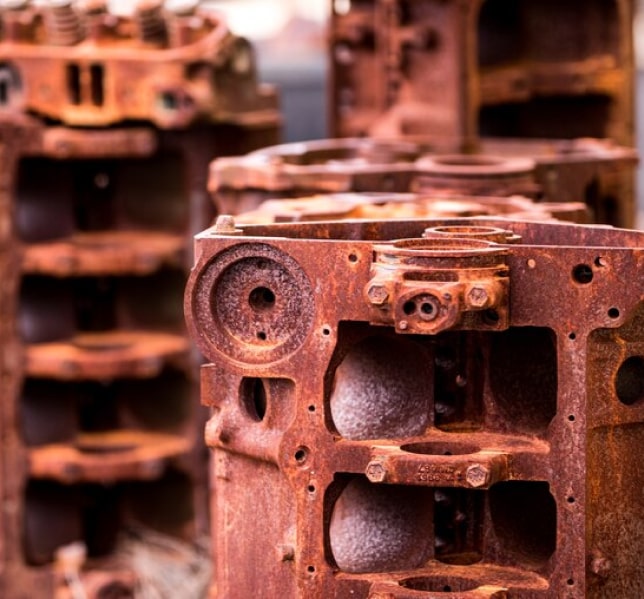

The all-pervasive phenomenon of metal corrosion is an irretrievable loss of metal affecting critical infrastructure and vital installations, not to speak of our everyday lives. It leads to
Massive monetary loss estimated at 5% of national GDP
Structural instability threatening safety
Significant environmental degradation through carbon emissions in structural replacement
Depletion of vital natural resources such as ores and fossils
Moreover, several studies have indicated mechanical and chemical methods of surface preparation and steel scrappage directly impact carbon footprint. The toxic discharge of corrosion inhibitors and harmful chemical constituents of protective coatings also contribute to environmental degradation.
All these problems have been exacerbated due to rampant industrialization with unrestrained polluting emissions. Proper redressal of this problem requires recognition of the electrochemical nature of metals and their alloys, both ferrous and non-ferrous, in relation to the environment of exposure, in particular, their vulnerabilities to acidic, alkaline, and saline conditions.
Electrochemical corrosion occurs when metal dissolves (anodic reaction) and corrosion products form (cathodic reaction) in the presence of liquids and air. The environment together with the specific type of metal play a role. Things like the gases and liquids around, like acids or salt affect corrosion. Other factors like humidity, wind speed, and the type of ions in the liquid can influence corrosion.
Limitation of Existing Coating Solutions
Barrier protective coatings with epoxies as their mainstay are normally prevalent. These provide good to excellent chemical resistance but have serious limitations in corrosion protection. As every coating contains some, albeit limited pathways of electrolyte diffusion into the coating-metal interface through its pores, barrier property alone is insufficient to stem corrosion. Corrosion inhibitors incorporated in such coatings are often unevenly deposited on the metal surface leading to corrosion and pitting. Interfacial corrosion through electrolyte penetration prior to actual coating film detachment leads to metal loss and repeated metal surface preparation during maintenance.
This is not only expensive but will also lead to eventual replacement of painted structures. Zinc based paints/coatings are known to be susceptible to acidic and strongly alkaline attack leading to premature failures in such atmospheres. Even colour-coated galvanized and Galvalume sheets have been found wanting in roofing and cladding applications in industrial installations when exposed to acidic fumes. Extensive surface preparation is absolutely vital for present day protective coatings both on new structural steel as well as pre-painted existing structures. Such preparation ideally calls for grit/shot blasting which is environmentally damaging, tedious, and often unsafe at industrial sites. Similarly galvanized structures (HDG) require elaborate surface preparation prior to paint application and painted structures are rapidly depleted of zinc in aggressive environments.
Approach to a Solution

Concept of metal passivation
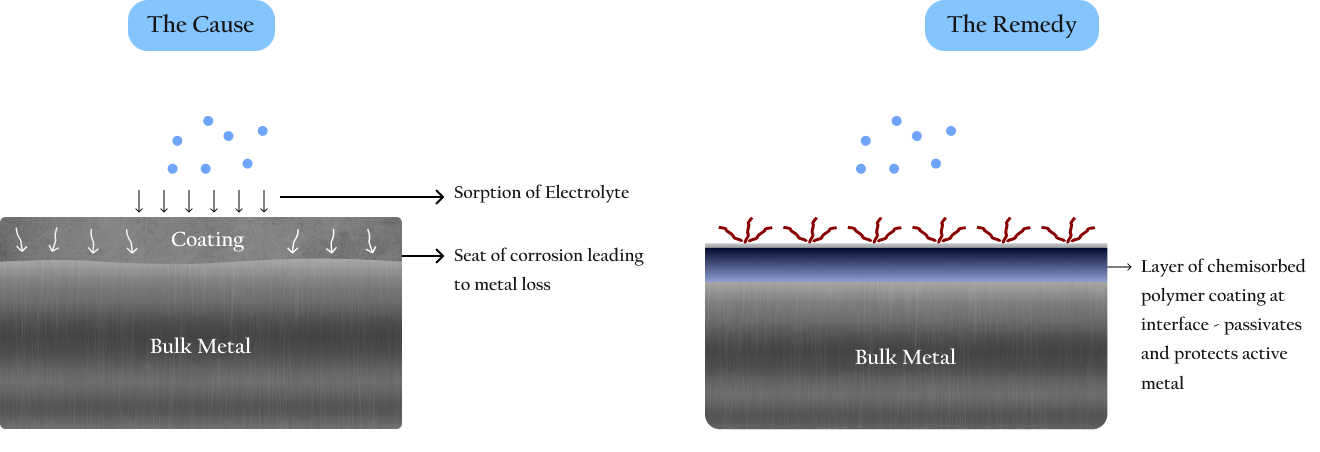
As electrolyte penetration can be impeded but not entirely thwarted, a viable method of metal passivation is the key to combat electrochemical corrosion. This would fundamentally alter the active metal interface and prolong life to the fullest possible extent. Moreover this will help reduce coating thickness and thus have a beneficial impact on adhesion. As active ‘white metal’ is highly prone to aerial oxidation such passivation should ideally be achieved even on oxidized ferrous and non-ferrous substrates.
Metguard achieves passivation on ferrous and non-ferrous metal substrates without accessing bare metal. Moreover, the passivation is a progressive transformation of protected structures, during exposure to hostile environments.
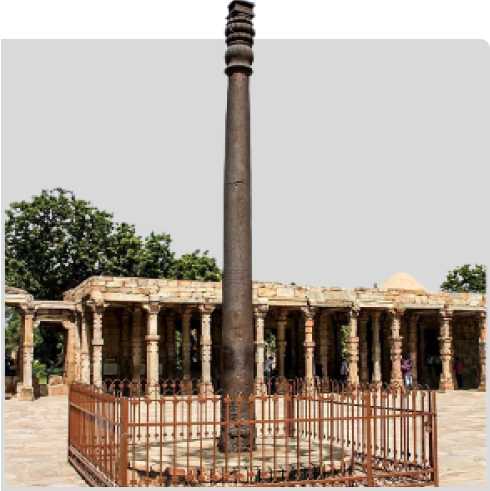
The science governing preservation of the famous Iron Pillar of Delhi for centuries, has been incorporated in Metguard corrosion protection.


The science governing preservation of the famous Iron Pillar of Delhi for centuries, has been incorporated in Metguard corrosion protection.

Concept of metal passivation
As electrolyte penetration can be impeded but not entirely thwarted, a viable method of metal passivation is the key to combat electrochemical corrosion. This would fundamentally alter the active metal interface and prolong life to the fullest possible extent. Moreover this will help reduce coating thickness and thus have a beneficial impact on adhesion. As active ‘white metal’ is highly prone to aerial oxidation such passivation should ideally be achieved even on oxidized ferrous and non-ferrous substrates.
Metguard achieves passivation on ferrous and non-ferrous metal substrates without accessing bare metal. Moreover, the passivation is a progressive transformation of protected structures, during exposure to hostile environments.
Estimating the extent of corrosion
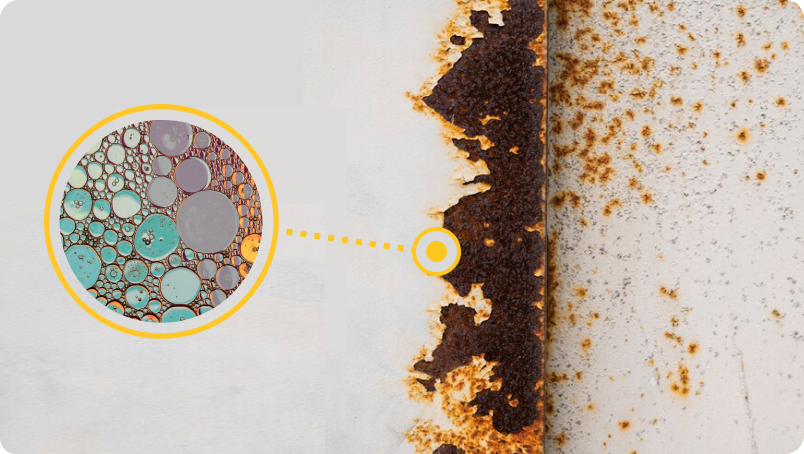
While many methods are prescribed for evaluating the corrosion resistance of painted metal, the most important measure of active metal loss is obtained by electrochemical impedance studies (EIS). A fair index of undercutting is obtained through creepage emanating from the scribe line in salt fog exposure. However, studies should include metal loss and adhesion on pre-rusted steel as being more representative of real-life situations in maintenance applications.
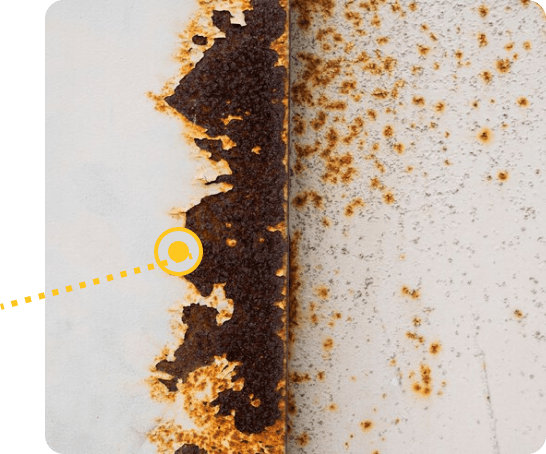

Estimating the extent of corrosion
While many methods are prescribed for evaluating the corrosion resistance of painted metal, the most important measure of active metal loss is obtained by electrochemical impedance studies (EIS). A fair index of undercutting is obtained through creepage emanating from the scribe line in salt fog exposure. However, studies should include metal loss and adhesion on pre-rusted steel as being more representative of real-life situations in maintenance applications.


Advantages Of Metguard
METGUARD coating scheme is characterized by
METGUARD coating scheme is
characterized by

No Metal Loss
No loss in thickness of the metal as it prevents undercutting and propagation of rust
Acid/Alkali Resistant
Exemplary performance in intensely corrosive atmosphere, acidic, alkaline, and saline
Exceptional adhesion to pre-rusted erected...
Exceptional adhesion to pre-rusted erected, as well as mill scale covered new steel, ferrous alloys, galvanized steel, steel coated with zinc-aluminium alloys, aluminium alloys etc. and thus elimination of rigorous grit/shot blasting techniques as a prelude to paint application
Outstanding resistance to dry heat (up to 200°C)...
Outstanding resistance to dry heat (up to 200°C) and thermal cycling
Toughness and high cohesive strength....
Toughness and high cohesive strength (scratch hardness of 3-5Kg – IS 101-pt.5;sec-2) in film thickness between 140 to 220 microns
Unmatched resistance to undercutting on steel...
Unmatched resistance to undercutting on steel and metalized steel and filiform corrosion on aluminium
Chromate, isocyanate, and halogen free...
Chromate, isocyanate, and halogen free eco-friendly technology
Simplified Application
Long Pot Life of more than 8 hrs without losing its efficacy
Minimum transfer losses
Unique nature of wet products ensures maximum transfer during application
Cost Effective
The ultimate protection cost will be much lower over life cycle of the structure
Application Areas
Structures made of Hot and Cold Rolled Steel, Hot Dip Galvanized Steel and Stainless steel, profiles of Aluminium alloys, and space age materials of construction
Rebars and other concrete embedded steel
Extension of longevity of existing pre- corroded structures without cumbersome surface preparation, such as grit/shot blasting
Roofing/cladding sheets in acidic areas – excellent replacement of pre-coated corrugated Galvanized/Galvalume sheets
Application Areas
Structures made of Hot and Cold Rolled Steel, Hot Dip Galvanized Steel and Stainless steel, profiles of Aluminium alloys, and space age materials of construction
Rebars and other concrete embedded steel
Extension of longevity of existing pre- corroded structures without cumbersome surface preparation, such as grit/shot blasting
Roofing/cladding sheets in acidic areas – excellent replacement of pre-coated corrugated Galvanized/Galvalume sheets